7 Warning Signs: What Level of RDW Is Dangerous
Discover what level of RDW is dangerous, why it matters for your health, and how to interpret RDW blood test results. Learn causes, risks, and answers to common FAQs in this expert guide.
Understanding RDW and Why It Matters
Red cell distribution width, more commonly known as RDW, is one of those blood test values that most people never think about until a doctor brings it up. Yet, this single marker can give deep insight into your health. It measures how much variation exists in the size of your red blood cells. Ideally, these cells should all be fairly uniform, but when the size starts to vary too much, it may be an early sign of an underlying problem.
Many people ask: what level of RDW is dangerous? The short answer is that extreme highs or lows can both be red flags, but the real story is more nuanced. The context of your overall health, your hemoglobin levels, and other blood test markers all matter. That’s why it’s not just about the number—it’s about the bigger picture of how your body is functioning.
What the RDW Test Actually Measures
When you get a complete blood count, RDW is one of the values that often gets overlooked. It doesn’t directly tell you how much oxygen your blood is carrying, but it gives clues about how well your bone marrow is producing healthy red blood cells. If there’s too much variability in size, it may suggest that something is interfering with red cell production, whether it’s a deficiency, a chronic condition, or even inflammation in the body.
Think of it this way: if every red blood cell were like a basketball, you’d expect them all to look about the same. But if you start mixing in tennis balls, golf balls, and beach balls, the distribution is all over the place. That’s exactly what happens in your bloodstream when RDW is abnormal—it becomes a mix of different-sized cells, which can compromise the efficiency of oxygen delivery.
What Level of RDW is Dangerous for Your Health
This is the most common concern people have: at what point does RDW become dangerous? While the reference range can vary slightly by lab, a typical healthy RDW falls between about eleven and fifteen percent. Levels that creep much higher often suggest underlying issues, while very low readings are less common but can still raise concerns.
An RDW that is significantly elevated often signals that red blood cells are not being produced consistently. It can indicate nutritional deficiencies like iron, vitamin B12, or folate shortages. It can also point to chronic diseases, inflammatory conditions, or bone marrow disorders. On the other side, unusually low RDW is rare but could suggest uniform cell sizes caused by other imbalances. Neither extreme should be ignored.
Why a High RDW Can Be Dangerous
When your RDW is too high, it doesn’t automatically mean you’re in immediate danger, but it does mean your body is trying to compensate for something. The production of uneven red blood cells means your oxygen transport system isn’t working as efficiently. This can lead to fatigue, shortness of breath, dizziness, or in severe cases, complications with heart and circulation.
A persistently high RDW has also been linked to more serious health risks. Studies have connected elevated RDW to higher chances of cardiovascular problems, kidney disease, and even increased overall mortality. While that may sound alarming, the real value of RDW is that it often gives doctors an early clue before things get worse.
Why a Low RDW Might Still Be a Concern
Most people only focus on high RDW, but very low readings are not always innocent. If your red cells are too uniform but you still feel unwell, it may mean your body is producing cells that are all the same size but not necessarily healthy. In such cases, it’s not the distribution but the quality of the cells that may be at issue.
Although a low RDW is not usually dangerous by itself, it shouldn’t be dismissed. If you have other abnormal blood values, your doctor may investigate further to rule out hidden conditions. That’s why context is everything when interpreting RDW results.
RDW and Its Relationship with Other Blood Tests
RDW doesn’t act alone. It becomes more meaningful when viewed alongside markers like mean corpuscular volume (MCV), hemoglobin, and hematocrit. For example, a high RDW combined with low MCV often points toward iron deficiency anemia. On the other hand, high RDW with high MCV may indicate vitamin B12 or folate deficiency.
This interplay is why doctors rarely make conclusions based on RDW alone. Instead, they look at the overall pattern of your blood test results, your symptoms, and sometimes additional testing. If your doctor highlights your RDW as a concern, it’s usually because it fits into a broader picture of your health.
Common Causes Behind Dangerous RDW Levels
There are many reasons RDW can be elevated or altered. Some of the most common include:
| Possible Cause | How It Affects RDW |
|---|---|
| Iron deficiency | Creates smaller red blood cells mixed with normal ones |
| Vitamin B12 deficiency | Produces larger cells alongside normal ones |
| Chronic inflammation | Disrupts normal red cell production |
| Bone marrow disorders | Leads to irregular and inconsistent red cells |
| Liver disease | Affects metabolism of nutrients needed for cell production |
When trying to understand what level of RDW is dangerous, knowing the cause is just as important as the number. A mildly elevated RDW from temporary stress or diet changes may not be as concerning as a persistently high RDW caused by an underlying chronic condition.
Lifestyle Factors That Influence RDW
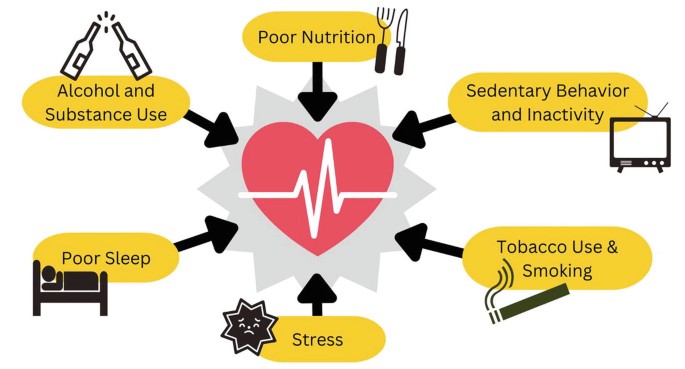
It’s not always disease that drives abnormal RDW. Lifestyle plays a big role as well. Poor nutrition, especially diets low in iron, folate, or vitamin B12, can cause fluctuations. Chronic alcohol consumption, smoking, and lack of exercise can also contribute to changes in blood cell production and distribution.
On the flip side, positive lifestyle habits can help stabilize RDW. Eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, getting enough sleep, and reducing stress all support healthy red cell production. While these changes may not fix underlying medical conditions, they can improve the efficiency of your blood system and reduce unnecessary risks.
How Doctors Respond to Dangerous RDW Levels
When your RDW falls outside the normal range, doctors don’t just focus on the number itself. They ask about your symptoms, review your history, and may order additional tests. The next steps often involve checking nutrient levels, assessing organ function, and sometimes performing imaging or bone marrow evaluations if a serious condition is suspected.
Treatment usually targets the underlying cause rather than the RDW directly. For example, if iron deficiency is the culprit, iron supplements and dietary changes are recommended. If chronic disease is behind the abnormal RDW, managing that condition becomes the priority.
Quotes from Medical Experts on RDW
“RDW is like a red flag waving in the background. It’s not always the disease itself, but it tells us when to look closer.” – Hematology Specialist
“An abnormal RDW rarely tells the whole story, but combined with other markers, it can uncover hidden problems early.” – Clinical Pathologist
These expert insights reinforce that while the number matters, it’s always part of a larger diagnostic puzzle.
Frequently Asked Questions about RDW
What level of RDW is considered dangerous?
Typically, an RDW above fifteen percent is considered concerning, especially if combined with other abnormal blood markers. However, the exact threshold depends on the lab and your overall health context.
Can a dangerous RDW level cause symptoms?
Yes. While mild changes may go unnoticed, significant abnormalities can lead to fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and shortness of breath. In severe cases, it can affect cardiovascular health.
Is a slightly high RDW always dangerous?
Not necessarily. Sometimes it reflects temporary stress or diet-related changes. What matters is whether it remains high over time and whether other blood test results are abnormal.
Can lifestyle changes lower RDW?
Yes, improving diet, hydration, sleep, and exercise can support healthy red blood cell production. But if a medical condition is behind the abnormal RDW, treating that condition is essential.
Do I need treatment if my RDW is low?
A low RDW is rarely dangerous on its own, but if you feel unwell or have other abnormal lab values, your doctor may recommend further evaluation.
Conclusion
RDW is one of those blood test values that doesn’t get much attention until it’s abnormal. So, what level of RDW is dangerous? The answer depends on context, but significant deviations from the normal range—especially high RDW—can indicate deeper health issues. It’s not about the number alone but about the story it tells when combined with other test results and symptoms.
If your RDW is flagged as abnormal, don’t panic. Instead, work with your healthcare provider to understand the cause, address any deficiencies or underlying conditions, and make lifestyle adjustments that support your overall blood health. In many cases, RDW acts less like a final diagnosis and more like an early warning system—one that gives you the opportunity to take action before problems escalate.





